Pneumonia in newborns often presents with subtle or nonspecific symptoms. Therefore, parents should pay close attention to any unusual signs, ensure early medical evaluation, and take advantage of the “golden window” for treatment. Prompt diagnosis and timely care not only maximize safety for the infant but also help minimize long-term complications that could affect healthy growth and development.
Causes of pneumonia in newborns
Pneumonia in newborns is most commonly caused by bacterial pathogens such as Streptococcus species, Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli, and other Gram-negative bacteria. Pulmonary infection may occur before, during, or after birth.
Newborns can develop pneumonia during delivery if they inhale amniotic fluid or meconium that has been contaminated, or secretions from the maternal genital tract. Inadequate sterile technique during labor, neonatal resuscitation, or postnatal care also increases the risk of infection through contaminated instruments, the environment, or caregivers.
Preterm or low-birth-weight infants are at higher risk due to immature esophageal reflexes and irregular muscular activity, which predispose them to frequent gastroesophageal reflux. During breastfeeding, these infants may vomit or regurgitate; if milk is aspirated into the lungs, it can cause acute symptoms such as rapid breathing, shortness of breath, or cyanosis, and may lead to pneumonia depending on the amount aspirated.
Additionally, infections such as stomatitis, skin infections, or umbilical cord infections can spread and result in neonatal pneumonia.
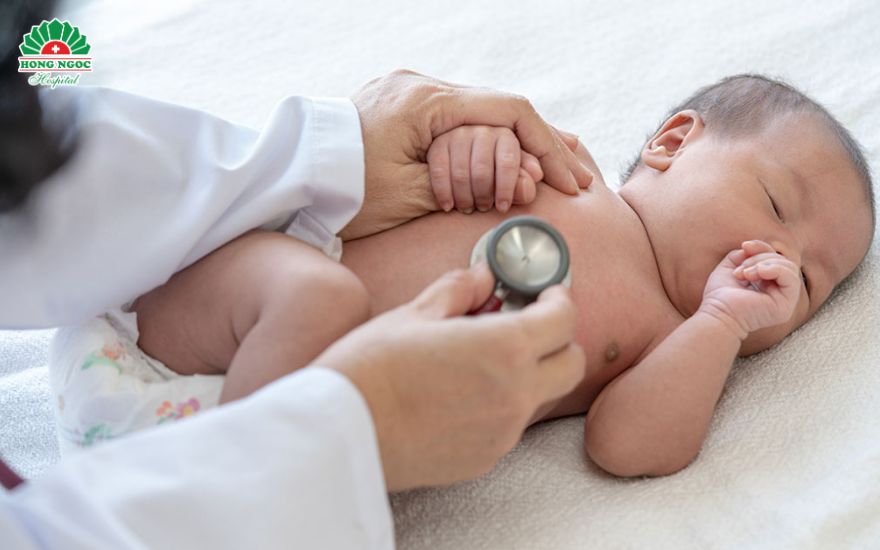
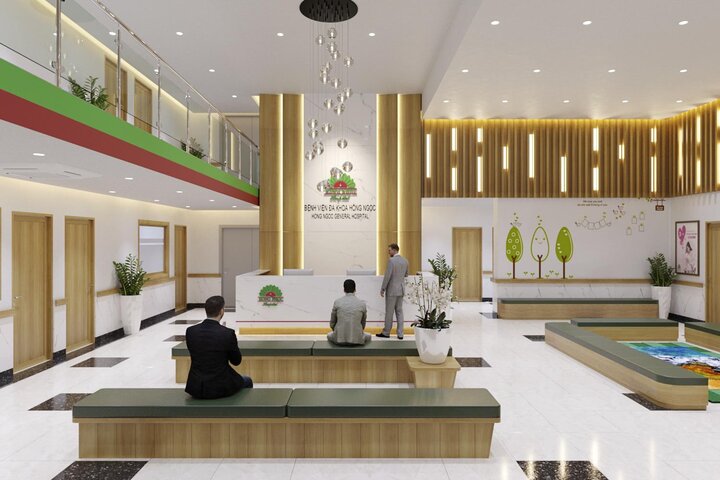
Signs of pneumonia in newborns
Unlike older children, who often present with typical symptoms such as high fever, frequent coughing, and wheezing sounds on auscultation, newborns usually show subtle and nonspecific signs because their respiratory system is not yet fully developed. These signs are easily overlooked.
Early signs of pneumonia in newborns may include:
- Poor feeding or refusal to feed
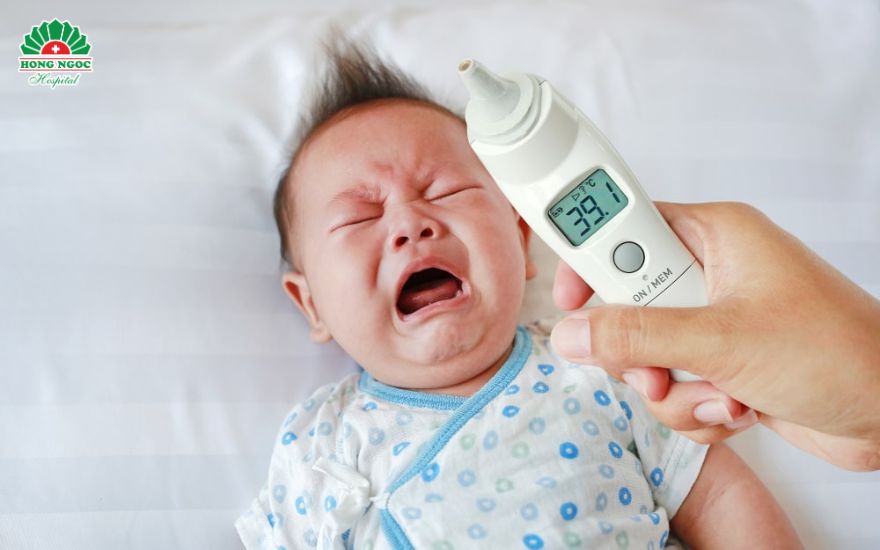
- Fever above 37.5°C or hypothermia
- Rapid breathing (over 60 breaths per minute) or signs of respiratory distress
When symptoms become more obvious, the disease is usually severe, with manifestations such as fever or hypothermia, lethargy, poor response to stimulation, poor feeding or refusal to feed, frequent vomiting, abdominal distension, difficulty breathing, chest retractions, or cyanosis.
Pneumonia in newborns tends to progress faster and more severely than in older children. In fact, many infants are brought to medical facilities without having a high fever or frequent cough, yet already present with severe pneumonia complications.
Therefore, parents and caregivers must closely monitor the infant’s condition. If a newborn shows early warning signs such as fever, refusal to feed, or rapid breathing, the child should be taken immediately to a healthcare facility for prompt evaluation and treatment to prevent life-threatening complications.
Reader may also be interested in:
- Pneumonia in children: Serious complications behind common symptoms
- What is pleuritis in children? Dangerous complications parents should be aware of
- How many types of respiratory tract infections occur in children? Recognizing common conditions and effective treatment approaches
How to prevent pneumonia in newborns
To reduce the risk of pneumonia in newborns, prevention should begin during pregnancy and continue after birth with proper care practices:
- Regular prenatal check-ups: Expectant mothers should attend routine antenatal visits, especially in the final trimester, to detect abnormalities early and ensure timely medical intervention if needed.
- Maintain body warmth after birth: Keeping the baby warm is one of the most important measures to protect newborn health.
- Exclusive breastfeeding: Breast milk strengthens the infant’s immune system. During feeding, mothers should be cautious to prevent aspiration, which can lead to respiratory complications.
- Hygiene practices: Caregivers must wash their hands with soap before and after handling the baby to reduce the risk of transmitting bacteria.
- Sterile and clean care items: Feeding utensils, clothing, blankets, and diapers must be kept clean, dry, and properly sterilized, while avoiding exposure to potential sources of infection.

Where to diagnose and treat pneumonia in newborns
With a team of pediatric specialists with more than 20 years of experience and a philosophy of safe, modern, and patient-centered care, the Pediatrics Department of Hong Ngoc General Hospital is a trusted address for the diagnosis and treatment of pneumonia in children.
- One-on-one consultation with senior experts: Each child is examined directly by pediatric specialists with over 20 years of experience, ensuring accurate identification of the underlying cause in a single visit and close monitoring throughout treatment.
- Advanced diagnostic imaging: Modern X-ray and CT scanners provide clear, high-resolution images, enabling the detection of deep-seated lesions for precise diagnosis.
- WHO-standard treatment protocols: Antibiotics are used judiciously—only in cases of secondary infection or acute respiratory failure—to minimize resistance and recurrence. Respiratory physiotherapy is incorporated to shorten recovery time and improve treatment outcomes.
- Strict infection control procedures: Comprehensive sterilization and separate patient pathways in both outpatient and inpatient areas ensure maximum safety, preventing secondary and cross-infections.
- Streamlined insurance process: Fast and simple procedures minimize waiting times for families.
- Five-star inpatient amenities: High-quality patient rooms, spacious play areas for children, and complimentary buffet vouchers provide comfort and convenience for both children and parents.
Note: The information provided in this article by Hong Ngoc General Hospital is for reference purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical diagnosis or treatment. For an accurate evaluation of your child’s condition, please visit a hospital for direct consultation and an individualized treatment plan from a physician.
PEDIATRICS DEPARTMENT – HONG NGOC GENERAL HOSPITAL
- 55 Yen Ninh, Ba Dinh, Hanoi
- No. 8 Chau Van Liem, Nam Tu Liem, Hanoi
- 3rd Floor, Building B, Tasco Mall, 07–09 Nguyen Van Linh, Long Bien, Hanoi
- 10th Floor, Keangnam Landmark 72, Pham Hung, Hanoi
- 1st Floor, TNL Plaza Goldseason, 47 Nguyen Tuan, Thanh Xuan, Hanoi
- 1st Floor, HPC Landmark 105, To Huu, Ha Dong, Hanoi
- Floors 1–3, Kosmo Tay Ho, 161 Xuan La, Bac Tu Liem, Hanoi
Free consultation and appointment hotline: 0947.616.006
>>> Stay updated with more useful information at: Pediatrics Department – Hong Ngoc General Hospital











