Coronary artery disease is one of the most common cardiovascular conditions and a leading cause of mortality in high-income countries. Gaining a clear understanding of the disease in order to seek early treatment or adopt preventive measures is essential to reducing the mortality rate associated with coronary artery disease.
What is coronary artery disease?
Coronary artery disease occurs when the blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of fatty plaques and other substances along the arterial walls. This leads to coronary artery narrowing or obstruction, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle.
The fatty deposits and other substances that accumulate along the inner walls of the arteries are known as atherosclerosis. As these deposits build up, they may form large plaques or break apart into smaller fragments, triggering an inflammatory response. As a result, the coronary arteries become narrower and stiffer, reducing blood flow to the heart. When the heart does not receive adequate blood and oxygen, patients may experience symptoms such as angina (chest pain) or myocardial infarction (heart attack).
This is a common condition that can lead to serious complications for patients and may even result in death.
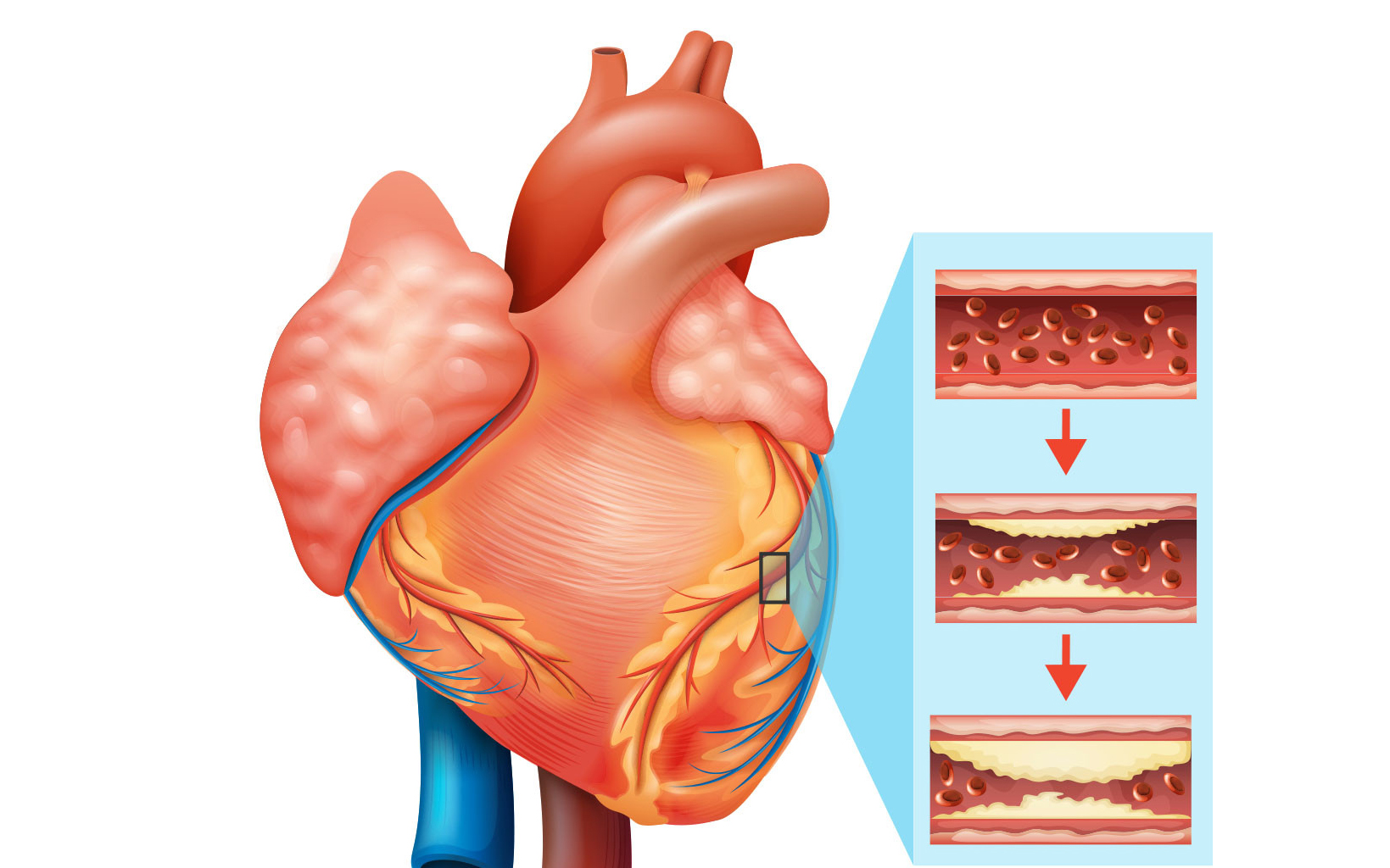
Causes of coronary artery disease
As mentioned above, the primary cause of coronary artery disease is the accumulation and progression of fatty plaques within the inner lining of the coronary arteries. However, the exact mechanisms underlying the formation and development of these plaques remain unclear. The following are several potential risk factors that may contribute to the development of coronary artery disease:
Unhealthy lifestyle: An unhealthy lifestyle can contribute to the development of atherosclerotic plaques and coronary artery disease. Diets high in fat and sugar, low in fiber, combined with little or no regular physical activity, significantly increase the risk.
Smoking: Both active smoking and passive exposure to secondhand smoke are major risk factors for coronary artery disease. The chemicals in tobacco can damage and inflame the inner lining of the arteries, promoting plaque formation.
Diabetes: Diabetes increases the risk of coronary artery narrowing due to the effects of elevated blood glucose levels and subsequent vascular damage.
Hypertension: High blood pressure exerts continuous stress on arterial walls, leading to damage and a greater likelihood of plaque buildup.
Genetics: A family history of coronary artery disease significantly increases an individual’s risk.
Age: The risk of coronary artery disease increases with age, as aging contributes to plaque accumulation and reduces the ability of blood vessels to repair themselves.
Other contributing factors: Elevated blood lipids, excess body weight, high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, reduced levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, and other conditions such as fatty liver disease may also play a role in the development of coronary artery disease.
Reader may also be interested in:
- What a cardiovascular examination entails and when to get a cardiac examination?
- Hypertension – a common condition with potentially serious complications
- Tachycardia: Causes and management
Symptoms of coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease may not cause noticeable symptoms in some individuals. However, when blood flow to the heart is restricted, patients may experience the following signs and symptoms:
Angina (chest pain)
This is the most common symptom of coronary artery disease. Patients may experience discomfort, pressure, tightness, or sharp pain in the chest. These episodes typically occur during physical exertion, exercise, or emotional stress, and often subside with rest or the use of nitrates.
Shortness of breath Coronary artery disease may cause shortness of breath during physical activity or even at rest. This occurs when the heart cannot supply enough blood and oxygen to other organs, including the lungs.
Fatigue Reduced blood flow to the body can lead to feelings of tiredness, weakness, and loss of energy.
Irregular heartbeat Some individuals with coronary artery disease may experience arrhythmias, such as rapid heartbeat, slow heartbeat, or irregular rhythms. This occurs when restricted coronary blood flow disrupts the heart’s electrical system.
Other symptoms Coronary artery disease may also cause nausea, vomiting, or discomfort in the chest.
Evaluation and diagnosis of coronary artery disease
To evaluate and diagnose coronary artery disease, the following methods and procedures are commonly applied:
Medical history and physical examination: The physician will review the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and risk factors such as family history, smoking, or alcohol use. A basic physical examination is then performed to check for signs and symptoms of coronary artery disease.
Blood tests: Blood tests are ordered to evaluate blood glucose, cholesterol, blood lipids, and other markers. Abnormal values may indicate coronary artery disease or its risk factors.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG records the electrical activity of the heart and can detect abnormalities such as arrhythmias or myocardial ischemia.
Imaging tests: Techniques such as echocardiography, computed tomography (CT) scans, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be used to provide detailed images of the heart and blood vessels, supporting the diagnosis of cardiovascular disease.
Exercise stress test: Tests such as treadmill or pharmacologic stress testing evaluate the heart’s response to exertion. These can help identify myocardial ischemia that occurs during increased activity.
Coronary angiography: This is the most definitive diagnostic method for assessing coronary arteries. A contrast dye is injected into the blood vessels, and X-ray imaging is performed to determine the degree of narrowing and whether interventional procedures are needed.
Based on the results of these assessments, physicians provide a final diagnosis of coronary artery disease and recommend treatment options tailored to the patient’s specific condition.
Treatment methods for coronary artery disease
There are several approaches to treating coronary artery disease, depending on the severity and specific condition of the disease as well as the overall health of the patient. The following are some common treatment options:
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthier lifestyle is a key component in the management of coronary artery disease. Specifically:
- Healthy diet: a fiber-rich and well-balanced diet, limiting saturated fats and foods high in cholesterol.
- Regular exercise: under medical guidance, such as walking, jogging, swimming, or aerobic activities.
- Weight management: losing weight when necessary.
- Risk factor control: managing high blood pressure, diabetes, and quitting smoking.
- Medications: Several types of medication may be prescribed to treat coronary artery disease, including:
- Nitrates: to relieve angina and improve blood flow to the heart.
- Antidiabetic agents: to control blood sugar levels in patients with diabetes, helping to prevent vascular damage.
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs (statins): to reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and prevent plaque buildup in the arteries.
- ACE inhibitors and calcium channel blockers: to control blood pressure and reduce strain on the heart.
- Aspirin and anticoagulants: to lower the risk of blood clot formation within the arteries.
- Coronary interventions: In more severe cases, when lifestyle changes and medications are insufficient, physicians may recommend coronary interventions, such as:
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG): creating a new pathway to bypass blocked or narrowed coronary arteries, restoring blood flow to the heart.
- Coronary stenting: inserting a small mesh tube (stent) into the narrowed artery to keep it open and maintain adequate blood circulation.
- Follow-up care: After treatment, ongoing management of coronary artery disease is essential. Patients should attend regular check-ups, monitor and adjust risk factors, and maintain a healthy lifestyle to prevent recurrence and disease progression.
Most importantly, patients should consult a trusted cardiology specialist to evaluate their condition and determine the most appropriate treatment plan. Medications must never be taken without a physician’s prescription and professional guidance.
The Cardiology Department at Hong Ngoc General Hospital is a trusted center for cardiovascular care, staffed by highly qualified specialists and equipped with advanced medical technologies. The department is dedicated to the early detection of coronary artery disease and the development of effective, individualized treatment protocols for every patient.
Register for a consultation with our cardiology specialists here:
Prevention of coronary artery disease
As with most cardiovascular conditions, the following measures are recommended to help prevent coronary artery disease:
Maintain a healthy lifestyle
- Follow a balanced diet rich in fiber, including plenty of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and foods high in omega-3.
- Limit saturated fats, high-cholesterol foods, sugar, and salt.
- Maintain a healthy body weight and avoid excessive weight gain.
- Reduce alcohol consumption and avoid smoking; ideally, quit completely.
Exercise regularly
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of physical activity per week, or about 30 minutes per day, depending on your health condition.
- Choose moderate activities such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, cycling, or joining aerobic classes.
- Consult your physician before starting any new exercise program.
Control blood pressure and blood sugar
- Have your blood pressure checked regularly and follow your treatment plan if you have hypertension.
- Manage blood sugar levels if you have diabetes by adhering to a proper diet and taking prescribed medications consistently.
Manage stress
- Practice stress management through relaxation methods such as yoga, meditation, light exercise, or engaging in enjoyable activities.
- Take time to relax and participate in hobbies or recreational activities.
Regular medical check-ups
- Schedule routine health check-ups to monitor blood pressure, blood sugar, cholesterol, and other cardiovascular indicators.
- Track your health metrics and seek medical advice regarding lifestyle adjustments or treatment when necessary.
Note: The information provided in this article by Hong Ngoc General Hospital is for reference only and should not replace medical diagnosis or treatment. Patients should not self-medicate. For an accurate assessment of your condition, please visit the hospital for direct examination, diagnosis, and appropriate treatment guidance from a physician.
Follow the official fanpage of Hong Ngoc General Hospital for more useful health information.