Otitis media is by no means “a childhood disease” as many people mistakenly believe. In adults, if not treated properly, middle ear infection can damage the eardrum and lead to hearing loss. So, what are the treatment options for otitis media in adults? And how can it be prevented? Let’s explore the answers in the article below.
Is otitis media in adults dangerous?
Otitis media in adults is less common than in children and generally carries a lower risk of serious complications. However, it still produces symptoms that can significantly affect daily life.
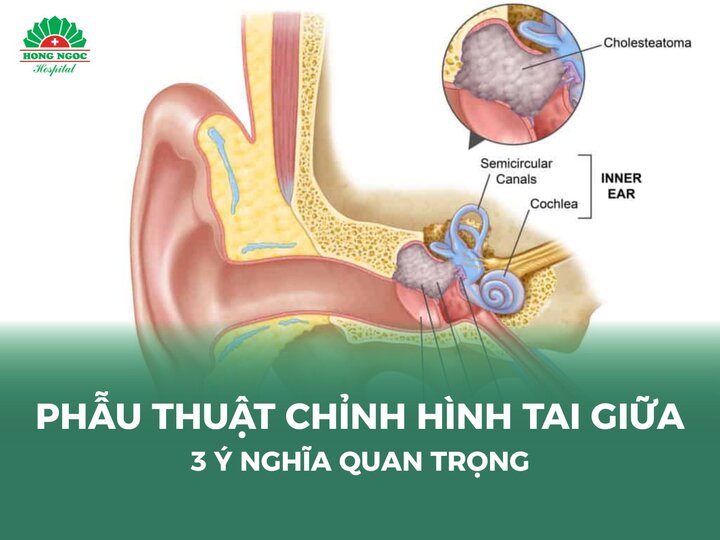
The condition is usually classified into two forms: acute otitis media and chronic otitis media. In cases where the disease progresses to chronic otitis media and complications such as mastoiditis or cholesteatoma occur, surgical intervention may be required to prevent permanent hearing loss.
Common symptoms of otitis media in adults include:
- Ear pain and discomfort: This is the primary and most common symptom of middle ear infection. Patients often describe a sharp or stabbing pain inside the ear. The pain may be persistent or occur suddenly, significantly disrupting daily activities.

- Tinnitus and hearing impairment: Middle ear infection often causes air to become trapped in the middle ear, leading to a sensation of ringing or fullness in the ear. Patients may feel that the ear canal is blocked, accompanied by discomfort and reduced or muffled hearing.
- Ear discharge: Fluid may drain from the ear in the form of pus, mucus, or a combination of both. Patients may notice moisture in the ear or experience the sensation of fluid flowing from the ear into the throat.
To accurately assess the condition of your ears or those of your loved ones, it is important to visit a reputable medical facility for thorough examination and professional consultation with ENT specialists. Schedule an appointment with our Ear–Nose–Throat experts via hotline 091.2002.131 – 0949.646.556 or register [HERE].
What causes otitis media in adults?
Several factors may lead to middle ear infection in adults, including:
- Upper respiratory tract infections: Conditions such as the common cold, influenza, or sinusitis can allow bacteria or viruses to spread and invade the Eustachian tube of the middle ear. This results in blockage of the tube, preventing normal drainage of mucus and air, and subsequently causes infection and inflammation of the middle ear.

- Severe respiratory infections: Conditions such as acute tonsillitis, pharyngitis, or pneumonia can spread and affect the eardrum, creating favorable conditions for bacterial invasion and middle ear infection.
- Exposure to smoke, dust, and chemicals: Smoking or frequent exposure to polluted environments can irritate the ear mucosa, promote infection, and obstruct the Eustachian tube.
- Poor ear hygiene or accidental trauma: The use of hard or sharp objects to clean the ear may injure the eardrum or ear canal lining, making it easier for bacteria to enter and cause otitis media.
How is otitis media in adults treated?
Medical management
- Systemic antibiotics: For bacterial otitis media, systemic antibiotics remain the standard treatment to eradicate infection. The choice of antibiotic is tailored based on test results and the patient’s individual factors to maximize treatment effectiveness.
- Topical antibiotics: In some cases, when bacteria do not respond to systemic therapy or infection recurs, antibiotics may be administered directly into the middle ear to control infection and relieve symptoms.
Surgical interventions
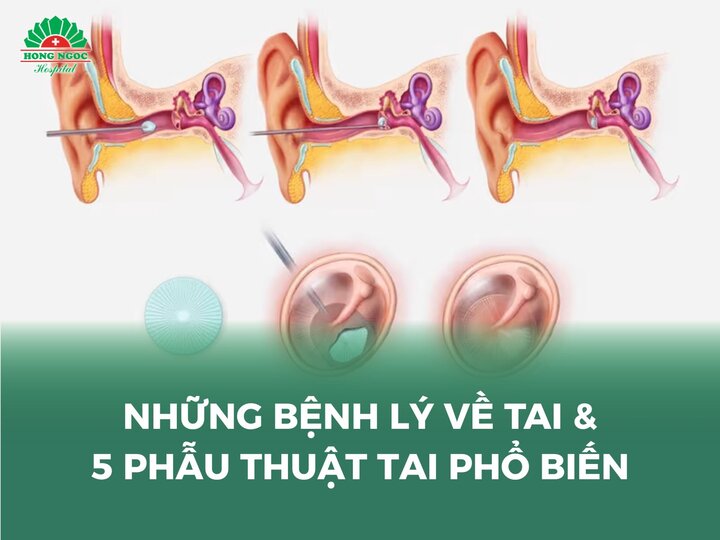
- Myringotomy with drainage: If otitis media results in excessive pus accumulation that cannot be controlled with medical therapy, a surgical procedure may be performed to drain fluid from the middle ear, relieving symptoms and reducing recurrence risk.
- Tympanoplasty (eardrum repair): In cases where the eardrum is perforated and does not heal spontaneously, surgical repair is indicated to restore the eardrum and improve hearing.
- Cholesteatoma surgery: Cholesteatoma is a noncancerous but destructive growth in the middle ear that can cause severe pain and hearing loss. If detected, surgical removal and reconstruction of the middle ear structures are necessary to prevent complications and preserve hearing.
Surgical treatment of otitis media at Hong Ngoc General Hospital
Each year, the Department of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery at Hong Ngoc General Hospital performs surgery for hundreds of patients with complications from chronic otitis media. Many of these patients have endured years of ear pain, while others present with large cholesteatomas causing eardrum perforation or even significant hearing loss.
A common feature of these cases is the need for combined surgical approaches—not only to completely remove the infected tissue and discharge but also to reconstruct the eardrum and restore middle ear structures. Throughout the procedure, surgeons take meticulous care to protect surrounding structures and preserve the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII), thus avoiding complications such as facial paralysis.
The hospital’s ENT surgeons have undergone advanced training in the UK, Singapore, and South Korea. They are proficient in the latest techniques and employ state-of-the-art technologies, including high-powered surgical microscopes, advanced endoscopic systems, and multifunctional drilling and dissection devices. These innovations ensure maximum precision, safety, and effectiveness in every procedure.
Reader may also be interested in:
How to prevent otitis media in adults
Otitis media in adults can be largely prevented by adopting the following measures:
- Avoid exposure to smoke and pollutants: Cigarette smoke, dust, and other irritants can damage the ear mucosa and obstruct the Eustachian tube. Limiting exposure helps reduce the risk of infection.
- Prevent colds and flu: Since otitis media is often associated with upper respiratory infections, it is advisable to avoid close contact with people who have colds, wear a mask when necessary, and keep the body—especially the ears—warm in cold weather.
- Seek prompt treatment for acute otitis media: At the first signs of infection such as ear pain, discharge, or hearing loss, consult an ENT specialist for timely diagnosis and management. Early treatment helps prevent the condition from progressing to chronic otitis media, thereby reducing the risk of complications and recurrence.
- Avoid unsafe ear cleaning: Using sharp or hard objects to clean the ears can injure the eardrum and ear canal lining, creating an entry point for bacteria. Instead, patients should avoid self-cleaning and seek medical guidance on safe ear care if they feel blocked or uncomfortable.
Contact Information
DEPARTMENT OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY (ENT) – HONG NGOC GENERAL HOSPITAL
- Address:
- No. 8 Chau Van Liem, Nam Tu Liem, Hanoi
- No. 55 Yen Ninh, Ba Dinh, Hanoi
- Hotline: 091.2002.131 – 0949.646.556
Note: The information provided in this article by Hong Ngoc General Hospital is for reference only and is not a substitute for medical diagnosis or treatment. To determine your exact condition, please visit a reputable healthcare facility for direct examination and receive a personalized treatment plan from qualified physicians.
Stay informed and improve your ENT health knowledge by following the official ENT and Head & Neck Surgery fanpage – Hong Ngoc General Hospital.